Introduction
We love what we do.
Our vision is
to co-design and co-build a cross-continental federated e-infrastructure and virtual research environment for global cooperation and open science by harmonized policies, interoperable protocols, transparent services and sustained mechanism.
Learn moreOpen infrastructure is one of the vital components within open science (UNESCO,2020). By harnessing the most advanced research facilities and software, open infrastructure is to handle those massive cross-disciplinary research resources. There’re already many e-infrastructures around the world, notably the European Open Science Cloud from the European Commission, New Digital Research Infrastructure Organization in Canada, the CSTCloud from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the ARDC e-infrastructure in Australia, XSEDE and other research e-infrastructure related initiatives in the US, the African Open Science Platform, etc.
Among all of these notable research e-infrastructures, we see the great potentials by better connectivity and interoperability between each other. What if we can have an open science cloud connecting more and more existing research facilities around the globe? The idea of a Global Open Science Cloud (GOSC) was initiated during the CODATA 2019 Beijing conference. The mission of GOSC is to interconnect different institutional, national and regional open science clouds and platforms to create a global virtual environment for globalized research and innovation. It aims to provide better ways to fully harness the global scientific research resources, and to help bridge the divide in infrastructure, technique, and capacity building among different countries, regions, and institutions.

About CAS GOSC project
To strengthen the capacity of connectivity and interoperability between different research platforms, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) granted seed funding in early 2021 to support a five-year international pilot project entitled "GOSC Initiative." Strategic partnerships with CODATA and other worldwide open science information infrastructures have also been developed to expand the global network of the GOSC Initiative.
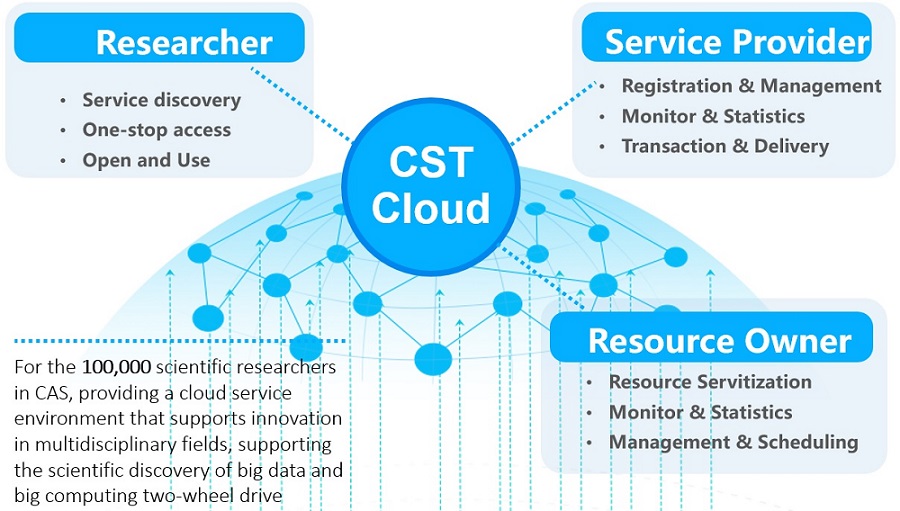
About CSTCloud & CNIC
With CAS funding and CNIC leadership, the CSTCloud team assumes the responsibility for integrating the cyberinfrastructure inside and outside academia, underpinning the fundamental technical infrastructure of the GOSC project. Taking advantage of the cloud computing technology, its main task is to construct and operate the cloud infrastructure monitoring platform and moderately develop the remote monitoring of the basic resources at research institutions. In addition, CSTCloud is obliged to construct, operate and maintain the cloud service platform as well as various services based on cloud resources, e.g., email system service, video conferencing service, passport service of CSTCloud, document archiving service for working groups and conference organization platform. This GOSC testbed is developed and maintained by the CSTCloud technical team.
As China’s earliest provider of supercomputing service, CNIC plays a key role as the operation management center and the main northern node of China National Grid. As the constructor, operator and service provider of the scientific database of the CAS, CNIC has established the largest research data storage facility and the basic data resource covering the broadest range of academic disciplines. In addition, CNIC serves as the constructor, operator and service provider of various important national systems such as China Science and Technology Cloud, National Data Sharing Service Platform for Basic Science, National Internet of Things Name Service Platform and Virtual Science Museums of China.

About GOSC Initiative
The GOSC Initiative is led by an international Advisory Board followed by a Steering Group for the design and implementation of all the tasks. An International Programme Office (IPO) has been established in the October 2022 to fulfil daily governance tasks assigned by the Advisory Board and the Steering Group. Initialized working groups, namely the Strategy, Governance and Sustainability, Policy and Legal, Technical Infrastructure, Data Interoperability have been established to carry on detailed work planned within the project. Another five early showcases are also arranged to demonstrate the maturity of the GOSC testbed and lead to open discussion and call for broader engagement in the long run.
Space physics: Incoherent scatter radar data fusion and computation
Biodiversity and Ecology: An open cloud service for camera trap data management and intelligent analysis
Earth sciences: SDG-13 climate change and natural disasters
Population health: Sensitive data federation analysis model in population health
Diffraction Data: Open reproducible raw diffraction data for access in pandemics
